Energy Storage Compliance and Deployment Services
As energy storage systems move from pilot applications to large scale deployment, long term operational stability depends not only on equipment performance, but increasingly on whether installation safety, regulatory compliance, and verification requirements are fully addressed at the design stage.
Drawing on extensive practical experience, Billion Watts has a strong command of the IEC 62933-5-2 safety requirements and the associated Verification Process for Compliance (VPC). We support clients in navigating regulatory frameworks and completing all required compliance procedures from design review through on site testing and final verification, ensuring energy storage systems are deployed safely, compliantly, and with long term operational reliability in mind.
Proven compliance expertise and regulatory credentials
Government Policy and Regulatory Framework
Net-zero transition has become a shared global direction for energy development. Taiwan has likewise set net-zero emissions by 2050 as a long-term national target, and continues to advance power system transformation and structural adjustment of its energy mix. In recent years, policy priorities have focused on enhancing grid resilience and deploying key technologies such as energy storage, supported by grid infrastructure investment and regulatory design to enable the stable integration of renewable energy and distributed energy resources.
From a regulatory perspective, following the 2025 amendment to the Electricity Act and the formal inclusion of Specified Electricity Supply Enterprises within the regulatory framework, emerging resources such as energy storage and demand response have been clearly established within Taiwan’s legal system. Through licensing reviews, the Verification Process for Compliance (VPC) for energy storage sites, and related operational management requirements, the government is guiding the industry from pilot applications toward institutionalized and scalable development, ensuring that power market participation and energy storage deployment operate on a compliant, safe, and reliable basis.
ESS Collaborate Mode
1. Willingness assessment
2. On-site investigation
3. Content description
4. Sign a contract
5. Review the design
6. Engineering construction
ESS Construction Processes

1. Case Preparation
Location Scouting, landowner lease, application for Taipower feeder, preparation and application for system impact, etc.

2. Energy Storage System Design and Planning
Owner contract execution, electrical and civil engineer drawing, project manager assignment, panel and main equipment procurement, etc.

3. Civil Engineering Construction
layout, weeding and land grading, site excavation, grounding system and piping works, RC foundation in equipment area, etc.

4. System Engineering and Testing
Weak current and high voltage power system engineering, EMS network monitoring system engineering, equipment positioning, testing before power transmission, etc.

5. Cooperate with Relevant Unit for The Final Acceptance
Acceptance of test items, system start-up test, acceptance of related data , Taipower transmission, education and training, etc.

6. O&M Team Takes Over
After-sales service, follow-up maintenance service of the case site, spare parts procurement and replacement operations, etc.
Guidelines for Enhancing Fire Safety Management of Energy Storage Systems
Issued by the National Fire Agency, Ministry of the Interior, Taiwan
Issued on 17 August 2022
The guidelines primarily apply to Front-of-the-Meter (FTM) grid-connected lithium-ion battery energy storage systems
1. Purpose of Installation and Core Compliance Requirements
Grid-connected energy storage systems are primarily deployed to provide ancillary services to the power system. In alignment with the regulatory framework introduced under the 2025 Electricity Act amendments, the installation and operation of such systems are formally regulated under the Specified Electricity Supply Enterprise regime.
Accordingly, projects are required to complete phased regulatory reviews, site verification under the
Verification Process for Compliance (VPC), and applicable land use and permitting procedures, ensuring that both grid operational requirements and regulatory obligations are met.
2. Site Selection Planning and Applicable Zones
Based on current regulations and practical experience, grid-connected energy storage is mostly preferentially installed in industrial parks or corresponding usage zones with relatively complete fire protection facilities and mature management conditions. Common feasible installation areas include:
- Designate industrial zones and science and technology industrial parks.
- Urban planning industrial zones (special, Class A, Class B).
- Apply for entry within the aforementioned industrial park, or set up within the factory area (including outside industrial parks) of a factory holding a valid factory registration certificate.
The actual conditions for setting up the facilities still need to be met on a case-by-case basis, and construction can only proceed after the land use, setting up review, fire protection and other related compliance procedures are completed.
Revised Version Issued on 3 November 2025
Expanded Scope to Behind-the-Meter (BTM) Energy Storage
(Including factories, commercial buildings, hospitals, and residential communities.)
1. Purpose of Installation and Core Compliance Considerations
- Application Benefits
Behind-the-meter (BTM) energy storage systems are primarily deployed to enhance power resilience, reduce peak demand and optimize contracted capacity costs, and provide backup power for end users.
Subject to customer contract terms and Taipower program eligibility, such systems may also be evaluated for integration with Energy Management Systems (EMS) to participate in demand response programs or related load management mechanisms, generating additional value streams. - Compliance Focus
BTM energy storage systems generally do not require an electricity business license. Their compliance focus is instead centered on electrical safety, fire safety certification, and equipment and system verification (such as VPC). At the early stages of each project, Billion Watts assists clients in assessing load characteristics and site conditions, incorporating real operational scenarios into the overall system design to mitigate compliance risks during both installation and operational phases.
2. Site Planning and Applicable Locations
- Installation Basis
Under current regulatory principles and industry practice, energy storage systems installed within existing factory premises are typically treated as ancillary facilities, with a valid factory registration certificate serving as the primary basis for lawful installation.
Actual applicability and approval, however, remain subject to the requirements of local competent authorities and project-specific review outcomes. - Asset and Insurance Considerations
At the design stage, Billion Watts integrates IEC/CNS 62933-5-2 safety verification standards and fire safety certification planning into the project framework.
This high-standard compliance-driven design approach not only enhances overall site safety, but also supports insurance risk assessment, improving the feasibility and robustness of property insurance coverage.
The Guidelines for Enhancing Fire Safety Management of Energy Storage Systems, revised and promulgated on 3 November 2025, have expanded their scope from the original focus on front-of-the-meter (FTM) grid-connected lithium-ion battery energy storage systems, as issued on 17 August 2022, to now include behind-the-meter (BTM) user-side energy storage systems.
This expanded coverage encompasses a wide range of deployment scenarios, including factories, commercial buildings, hospitals, and residential communities, marking Taiwan’s transition into a phase of comprehensive regulatory oversight and institutionalized fire safety management for energy storage systems.
Equipment Safety
Fire Safety
Billion Watts integrates CNS / IEC 62933-5-2 safety requirements, the Verification Process for Compliance (VPC), and the latest fire safety management guidelines at the early stages of each project. By holistically assessing fire protection, structural conditions, electrical systems, and real-world operational scenarios, we support project owners in achieving regulatory compliance while balancing safety, space efficiency, and long-term operational viability, thereby reducing retrofit requirements and operational risks over the project lifecycle.
Required Documentation
- Land and Building Use Authorization:Depending on the project owner’s status, documentation shall include proof of land or building ownership, or valid authorization granted by the owner. For government-managed sites or existing factory premises, approval letters issued by the competent authority or a valid factory registration certificate may be submitted, as applicable.
- Installation and Safety Compliance Documentation:In accordance with the latest regulatory framework effective in 2025, projects are required to complete a fire risk assessment, fire safety design, and relevant professional certifications. These documents form a key basis for installation approval and regulatory review.
- Equipment and System Verification Materials (as applicable):Subject to the installation type and review requirements, supporting materials such as equipment test reports, system verification records, or Verification Process for Compliance (VPC) documentation shall be provided.
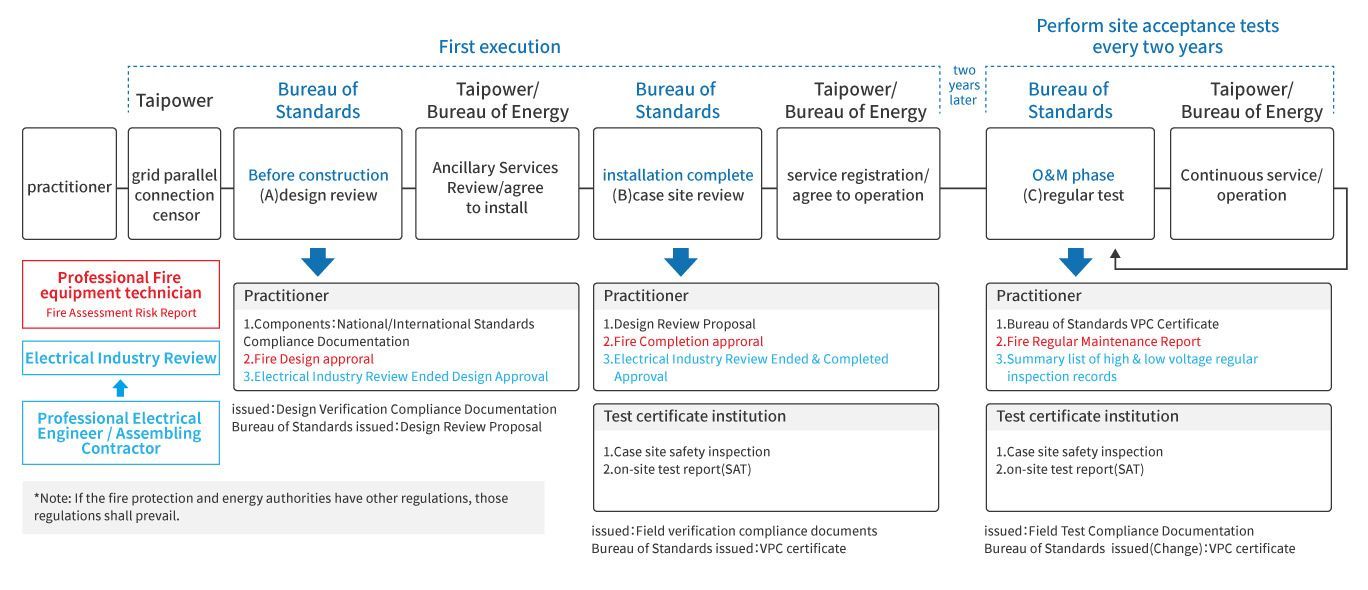
Energy Storage System Verification and Compliance Framework
Pre-Construction Phase
Design Review
Prior to construction, a Fire Risk Assessment (FRA) report must be completed, with system design prepared and certified by a licensed fire protection engineer.
The design shall comply with IEC/CNS 62933-5-2 safety requirements and the latest fire safety management guidelines. Construction may commence only after the design has been reviewed and approved by the relevant authorities.
Post-Construction Phase
Site Verification
Upon completion of construction, an on-site inspection shall be conducted, including fire safety completion certification and any required safety performance testing.
This review confirms that the as-built installation conforms to the approved design and safety requirements, and forms the basis for obtaining the Verification Process for Compliance (VPC) certification for the energy storage system.
Operation and Maintenance Phase
Ongoing Compliance and O&M Review
Once the system enters operation, a periodic VPC test is required every two years in accordance with regulatory requirements.
In addition, annual fire safety equipment inspections and emergency response drills must be conducted in compliance with fire safety regulations, ensuring continued system safety and long-term operational compliance.
ESS Verification Review System Process at Each Stage